| Cardiac | |
|---|---|
| GI | |
| Bone | |
| GU | |
| Neuro | |
| Peds | |
| Faculty | |
| Student | |
| Quizzes | |
| Image DDX | |
| Mobile | |
| |
Misc |
| Videocasts | |
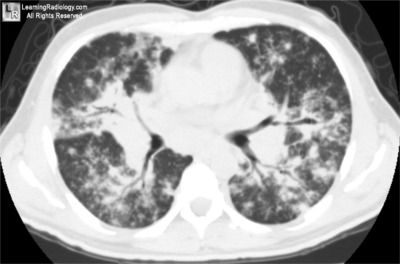
What's the most likely diagnosis?
- 47 year-old female with chronic cough
1. Silicosis
2. Congestive heart failure
3. Alveolar sarcoid
4. Castelmann's Disease
5. Rickets
Additional Image - Axial CT image of the chest
![]()
Answer:
3. Alveolar Sarcoid
.
.
More (Click Discussion Tab)
Alveolar Sarcoid
General Considerations
- Least common manifestation of sarcoid in the lungs (2%)
- Several large airspace “masses” frequently with air bronchograms
- Occurs when granulomas become confluent and compress airspaces
.
This Week
Test your skills in differentiating between accurate and inaccurate conclusions based on your observations ("good calls" versus "pitfalls".) Learn how to avoid the pitfalls. There is a mini-quiz at the end. |
Review descriptions of key imaging signs in the shorthand of Tweets by subscribing to this new LearningRadiology Twitter feed for your computer or cell phone
|
Key points on recognizing the most common fractures and dislocations |
Basic CT imaging of the brain focusing on the findings of cerebrovascular accidents |
The top diagnostic imaging diagnoses that all medical students should recognize according to the Alliance of Medical Student Educators in Radiology |
Recognizing normal and key abnormal intestinal gas patterns, free air and abdominal calcifications |
Some of the fundamentals of interpreting chest images |
| LearningRadiology.com |
is an award-winning educational website aimed primarily at medical students and radiology residents-in-training, containing lectures, handouts, images, Cases of the Week, archives of cases, quizzes, flashcards of differential diagnoses and “most commons” lists, primarily in the areas of chest, GI, GU cardiac, bone and neuroradiology. |